SAP-Sales & Distribution (SD)
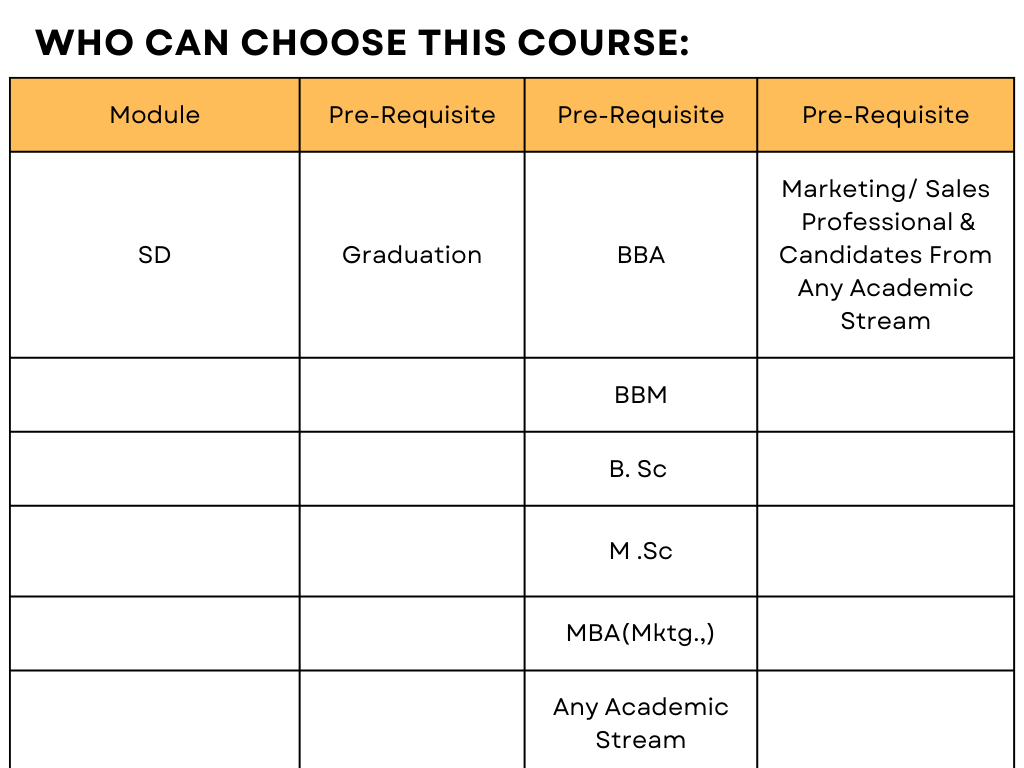
Sales & Distribution (SD) is a Functional Module which caters to Sales Function of a Business Organization. Sales and Marketing professionals who would like to learn SAP and enter into IT industry can choose SD Module. Apart from the above experienced professionals, people who are graduated with MBA, BBA, BBM etc., degrees are also more relevant for SD Module. As people from all Academic streams like B.Com, MBA, B.Sc., and even M.Pharmacy, M.Tech, are relevant to enter into Sales or Marketing profession, there is no entry barrier, academically, to learn and become Sales & Distribution (SD) Consultant. SD Module is one of the prominent Modules of SAP which has more jobs than that of any other Module of SAP. This is an evergreen Module where you can find jobs always, irrespective of Industry or Country.

Eligibility for a course typically depends on the following:
- Prerequisites: Required prior courses or skills.
- Level of Study: Undergraduate, graduate, or continuing education.
- Program Requirements: Specific to your major or program.
- Open Enrollment: Available to all students as an elective.
- Special Permissions: Might need instructor or department approval.
- Availability: Limited seats may give priority to certain students.
- Location/Delivery: Online or specific campus availability.
Check the course catalog or consult with an academic advisor for specifics.
SAP-SD COURSE CONTENT
Session 1: Introduction
1. Introduction to SAP
2. Landscape of SAP
a. Two-System Landscape
b. Three-System Landscape
3. Architecture of SAP
4. Introduction to SAP SD
a. Sales Area
b. Sales Organization
c. Division
d. Distribution Channel
e. Sales Group
f. Sales Office
Session 2: Enterprise Structure
1. Introduction to Organization Structure
2. General Sales and Distribution Structures
3. Definition and Assignment of Organizational elements
Session 3: Master Data in Sales and Distribution process
1. Customer Master Data
a. General Data Section
b. Company Code Data Section
c. Sales Area Data Section
2. Account Groups
3. Number Ranges
4. Material Master Data
5. Customer Material Info Record
Session 4: Sales Documents
1. Sales Document Header Category
2. Sales Document Item Category
3. Sales Document Schedule Line Category
4. Inquiry
5. Quotation
6. Standard Order
7. Cash Sales
8. Rush Order
Session 5: Customer Complaints
1. Customer Returns
2. Debit Memo Request
3. Credit Memo Request
4. Free of charge Delivery
5. Subsequent Free of Charge Delivery
Session 6: Basic Functions
1) PRICING:
a) Pricing Process:
• Condition Tables
• Access Sequence
• Condition Types
• Pricing Procedure
• Pricing Procedure Determination
Condition Record Maintenance
b) Condition Supplement
c) Item Conditions
d) Header Conditions
e) Palette Discounts & Surcharges
2) Free Goods Determination
a) Inclusive Method
b) Exclusive Method
3) Revenue Account Determination
4) Partner Determination
5) Output Determination
6) Material Determination
7) Material Listing / Exclusion
8) Credit Management
9) Route Determination
10) Tax Determination
11) Incompletion Procedure
12) Transfer of Requirements (TOR)
13) Availability Check
Session 7: Delivery
1. Delivery Document Header Category
2. Delivery Document Item Category
3. Number Ranges
4. Shipping Point Determination
5. Delivery Scheduling & Transportation Scheduling
6. Packing
Session 8: Billing
Session 9: Special Business Process
1. Intercompany Sales
2. Third Party Order Processing
3. Individual Purchase Order
Session 10: Cross-Functional Integration
1) FICO Integration with SD Module:
a. Tax Determination
b. Credit Management
c. Revenue Account Determination
d. Delivery
e. PGI (Post Goods Issue)
f. Billing
2) MM Integration with SD Module:
a. Transfer of Requirement (TOR)
b. Availability Check (OR)
Session 11: Cross-Applications
1. ASAP Methodology :
a. Project Preparation
b. Business Blue Print (BBP)
c. Realization
d. Final Preparation
Go-Live & Support
Session 12: S/4 HANA – Overview
